Mean, Median, Mode
| Term | Definition |
|---|
| Mean |
The mean is the sum of all values divided by the number of values.
It is similar to average. |
| Median |
Median is literally the middle value. If you listed all the values in numerical order, the middle value is the median.
If there are two middle values, then the median is the average of these two middle values. |
| Mode |
Mode is the value that is most common in a set of data.
There can be more than one mode in a set of data. |
| Range |
Range measures the span of values in the data.
It is the difference between the largest and smallest values of the data. |
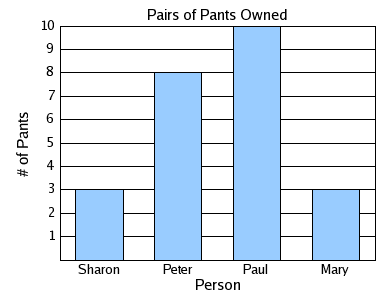
Example 1: Bar graph
The data set is {3, 8, 10, 3}.
Mean:
3 + 8 + 10 + 3
4 |
= |
24
4 |
= |
6 |
Median:
Listing the data values in order, we get 3, 3, 8, 10.
The middle values are 3 and 8.
Mode:
The value 3 occurs the most in the data set.
Range:
The largest value in the data set is 10 and the smallest value in the data set is 3.
10 - 3 = 7
Example 2: Table - no mode
The data set is {98, 69, 79}.
Mean:
98 + 69 + 79
3 |
= |
246
3 |
= |
82 |
Median:
Listing the data values in order, we get 69, 79, 98.
The middle value is 79.
Mode:
Each value only occurs once in the data set. There is no mode for this data set.
Range:
The largest value in the data set is 98 and the smallest value in the data set is 69.
98 - 69 = 29
Example 3: Multiple modes
The data set is {4, 15, 6, 6, 4}.
Mode:
Both 4 and 6 occur twice in the data set. The modes are 4 and 6.
Math Score homepage